A Comprehensive Guide to Shoulder Pain: Causes, Conditions, and Care
Shoulder pain is a common ailment that can significantly hinder one’s ability to perform daily activities or enjoy sports and exercise. This detailed guide explores the various causes of shoulder pain, common conditions, and effective shoulder pain treatment options to help you understand and manage this discomfort.
Understanding Shoulder Pain
The shoulder, being one of the most flexible joints in the body, is prone to a wide range of injuries and conditions. These injuries can be attributed to athletic activities that involve excessive, repetitive overhead motions, such as swimming, tennis, and weightlifting, as well as everyday tasks like washing walls, hanging curtains, and gardening.
Key Questions to Consider:
- Is your shoulder stiff, limiting your arm’s normal range of motion?
- Does it feel like your shoulder could pop out of its socket?
- Are you lacking the strength in your shoulder to carry out daily activities?
If you answered “yes” to any of these questions, seeking medical help to determine the severity of your condition is crucial.

Common Conditions That Cause Shoulder Pain
AC Separation & Frozen Shoulder:
Conditions like AC separation and frozen shoulder result from injuries or gradual wear, leading to pain and limited mobility.
Glenohumeral Arthritis & Labral Tears:
Arthritis and labral tears can deteriorate your shoulder’s health, causing chronic discomfort and instability.
Rotator Cuff Impingement & Tear:
These are among the most common issues, often resulting from overuse or acute injuries, leading to severe pain and functional limitations.
Shoulder Dislocation & Trauma:
A direct impact or fall can dislocate the shoulder, necessitating immediate medical attention to restore stability and function.
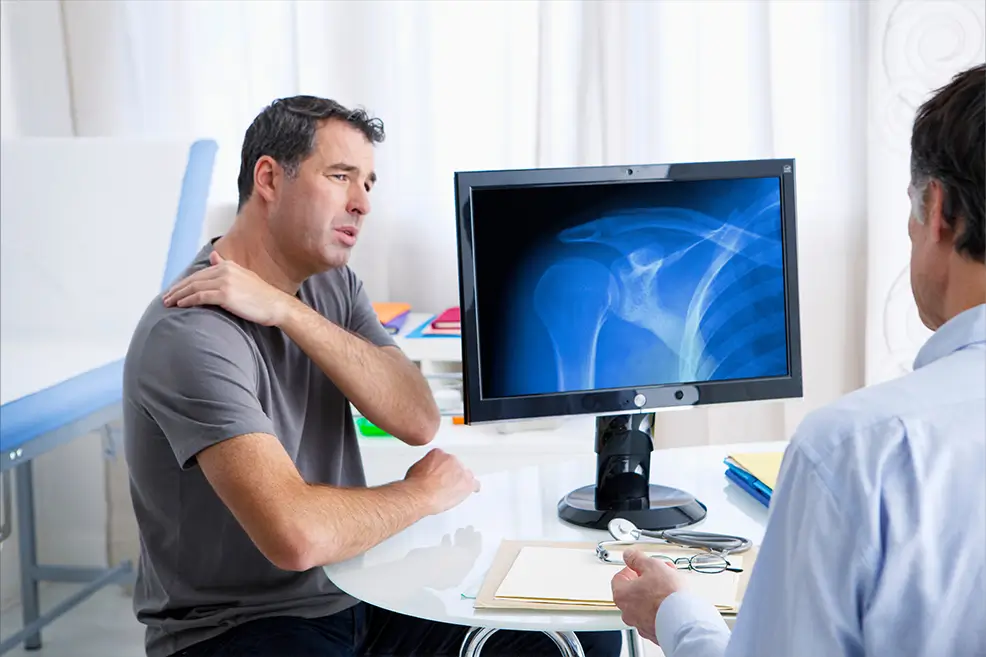
Identifying the Shoulder Pain Causes
While many shoulder problems involve the bones, a majority of issues are related to the soft tissues—muscles, ligaments, and tendons. These problems typically fall into three major categories:
- Tendinitis/Bursitis: Often a result of overuse or aging, causing inflammation and pain.
- Injury/Instability: Movement or impact forces the shoulder out of its normal position, leading to dislocation and instability.
- Arthritis: Degenerative changes cause inflammation, swelling, pain, and stiffness.
Tendinitis:
A wearing process, similar to the sole of a shoe splitting from overuse, tendinitis can be acute or chronic, significantly impacting shoulder movement and stability.
Rotator Cuff Tears:
With the shoulder’s extensive range of motion, it’s at high risk for overuse and tearing, especially in individuals over 40. Non-surgical treatment like RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) can be effective for mild cases.

Bursitis:
Excessive use can lead to bursitis, an inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction in the shoulder, often occurring alongside rotator cuff tendinitis.
Injury/Instability:
Shoulder instability can result from the bones being forced out of their normal position, causing dislocations and a sensation of the shoulder slipping out of place.
Arthritis:
Various types of arthritis can wear down the shoulder joint, leading to swelling, pain, and restricted motion. Sports or work injuries often trigger this condition.

Managing Shoulder Pain
Treatments and Care:
Shoulder pain treatment varies depending on the underlying cause. Non-surgical options, including physical therapy, medication, and rest, can effectively manage many shoulder pain conditions. In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged tissues and restore function.
Preventive Measures:
Proper warm-up and stretching exercises before engaging in physical activities can significantly reduce the risk of shoulder injuries. Additionally, incorporating strength training and ergonomic adjustments into daily routines can help maintain shoulder health and prevent chronic shoulder pain conditions.
Conclusion
Shoulder pain, while common, should not be ignored. Understanding the potential causes and conditions associated with shoulder discomfort is crucial for seeking appropriate shoulder pain care and treatment. Whether your shoulder pain is due to an acute injury or a chronic condition, consulting with a healthcare professional can help you navigate the path to recovery and pain-free living.
Frequently Asked Question
The main causes of shoulder pain include injury, overuse, inflammation, arthritis, tendonitis, bursitis, or even referred pain from other areas such as the neck or spine.
Common shoulder pain conditions and disorders include rotator cuff tears, tendonitis (such as biceps tendonitis or supraspinatus tendonitis), bursitis, frozen shoulder, shoulder instability, arthritis (osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis), and shoulder impingement syndrome.
Treatment for shoulder pain depends on the underlying cause but may include rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroid injections, and in severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
Physiotherapy for shoulder pain focuses on strengthening the muscles around the shoulder joint, improving flexibility, and correcting posture and movement patterns to alleviate pain and improve function.
Recovery time for shoulder pain varies depending on the severity of the injury or condition, adherence to treatment, and individual factors. Minor shoulder injuries may heal within a few weeks with rest and conservative treatments, while more severe conditions may take several months or longer to fully recover.

